Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet often overlooked oral health condition. Many individuals dismiss early symptoms as inconsequential, not realizing the possible long-term effects on dental health. Left unmanaged, gum disease can affect the structure and function of teeth and gums over time, potentially causing a need for tooth replacement. Understanding the key aspects of gum disease will help you take appropriate steps for prevention.
What Is Gum Disease?
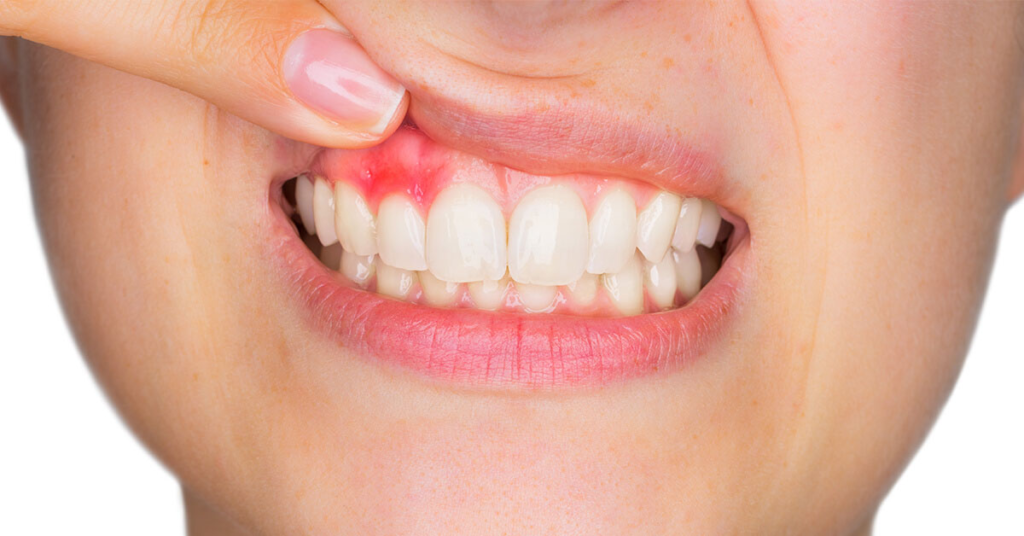
Gum disease is an inflammatory condition that affects the tissues supporting the teeth. It begins with untreated plaque buildup on teeth, which hardens into tartar. This tartar contains harmful bacteria that irritate the gums, leading to redness and swelling.
There are four stages of gum disease: gingivitis, mild periodontitis, moderate periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis. Gingivitis presents as gum inflammation and bleeding during brushing or flossing. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where gum recession, bone damage, and even tooth loss can occur at varying degrees through each stage.
Gum disease is not an isolated oral health problem. Its effects can extend beyond the mouth, potentially contributing to broader health complications. There are links between gum disease and systemic conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular issues.
What Are Its Causes and Symptoms?
The primary cause of gum disease is plaque buildup. This buildup occurs when food particles and bacteria are not adequately removed during brushing or flossing. Other contributing factors include smoking, genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, and certain medications. Poor oral hygiene and irregular dental checkups further increase the risk of developing gum disease.
Symptoms vary depending on the stage of the condition. Common early symptoms include swollen gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, or persistent bad breath. At more advanced stages, you may notice receding gums, loose teeth, or a change in how your teeth fit together when biting. Gum disease can often progress unnoticed, which makes dental visits integral to identifying it in its early stages. If you regularly experience any of these symptoms, prioritizing prompt dental care can prevent progression to more serious issues.
Can It Lead to Tooth Replacement?
One of the potential long-term effects of untreated gum disease is tooth loss, which can require future tooth replacement. Periodontitis damages the gum tissue and the bone that supports teeth. When this bone structure weakens, teeth can become loose or even fall out.
Losing teeth impacts more than just appearance. It also affects chewing, speech, and overall oral function. Missing teeth can cause surrounding teeth to shift, leading to further oral health complications. Tooth loss may eventually necessitate dental solutions such as dental implants, bridges, or dentures to restore proper function and aesthetics.
Gum disease progresses slowly, making early detection helpful for prevention. With timely care, stopping the condition before it causes lasting harm is possible. Regular dental checkups allow dentists or periodontists to identify signs of gum disease early and provide effective treatment. Taking these steps can help protect your oral health in the long term.
How Can I Prevent It?
Preventing gum disease often begins with consistent oral hygiene habits. Brushing your teeth twice daily for at least two minutes and flossing once a day are the foundation of a healthy routine. Antimicrobial mouth rinses can also help remove additional bacteria.
Routine dental checkups and cleanings are equally necessary. Professional cleaning removes plaque and tartar buildup in areas you may miss with brushing alone. This proactive approach helps maintain healthy gums and can detect gum disease at its earliest stages.
Lifestyle changes play a key role in improving gum health. Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of gum disease. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps strengthen your gums and overall oral health. Managing conditions like diabetes is fundamental for maintaining healthier gums over time.
Take Action for Healthier Gums
Gum disease can have serious consequences for overall dental health, especially when left untreated. By understanding its causes and symptoms and taking preventive measures, you can maintain healthy gums and avoid complications like tooth loss or the need for replacements. If you have concerns about your gum health, consulting a dental professional is a valuable next step. Regular care and attention can keep your smile strong and healthy for years to come.
Understanding QuantumRF Technology In Skin Rejuvenation
Skin rejuvenation can give skin a more youthful appearance, and QuantumRF is a modern advancement…
The Role of Regular Podiatry Check-ups for Overall Wellness
Foot health is a component of general well-being that may go unnoticed until problems arise….
Understanding the Role of a Plastic Surgeon in Cosmetic Procedures
Cosmetic procedures require careful planning, medical expertise, and a clear focus on safety and natural-looking…
The Connection Between Shingles and Your Immune System
Shingles is a viral condition caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same…
The Impact of Plantar Fasciitis on Daily Activities
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the thick band of tissue…
The Advantages of Choosing Laser Hair Removal
Laser hair removal is a common cosmetic procedure, and it uses concentrated light to target…